Embark on a journey into the realm of Cloud-Native Tech Solutions for Scalable Growth, where innovation meets scalability to drive businesses forward.
Learn about the transformative power of cloud-native technology and how it propels industries towards unprecedented growth and efficiency.
Introduction to Cloud-Native Tech Solutions for Scalable Growth
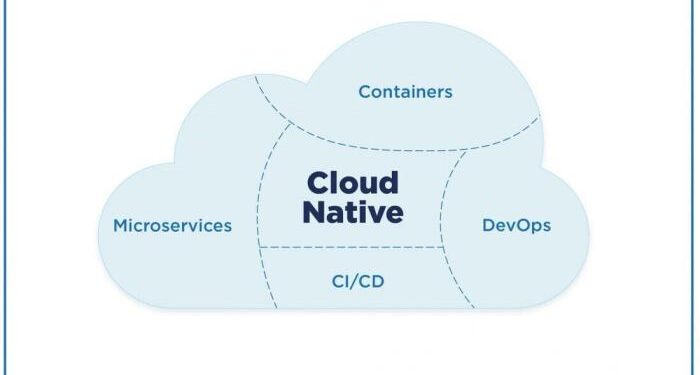
Cloud-native technology refers to designing and building applications that leverage the advantages of cloud computing to enhance scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. It involves utilizing containerization, microservices architecture, and DevOps practices to develop and deploy software in a cloud environment. Unlike traditional approaches, cloud-native solutions are specifically designed to take full advantage of the cloud's capabilities, such as auto-scaling, high availability, and rapid deployment.
This approach allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands and scale their operations without significant investments in infrastructure.Various industries have benefited from adopting cloud-native technologies for scalable growth. For example, e-commerce companies can handle spikes in traffic during sales events seamlessly, healthcare providers can securely store and analyze large amounts of patient data, and financial institutions can process transactions efficiently while ensuring data security and compliance.
Key Components of Cloud-Native Tech Solutions
Containerization, Microservices, Orchestration, Automation, Security
Cloud-native tech solutions are built on a foundation of key components that enable scalability, flexibility, and efficiency in modern software development. These components work together to streamline the deployment, management, and scaling of applications in cloud environments.
Containerization
- Containers encapsulate an application and its dependencies, allowing for consistent deployment across different environments.
- They provide isolation, portability, and scalability, making it easier to manage and scale applications in a cloud-native environment.
Microservices
- Microservices architecture breaks down applications into smaller, independently deployable services.
- Each service focuses on a specific function, improving agility, scalability, and fault isolation in cloud-native applications.
Orchestration
- Orchestration tools like Kubernetes automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- They ensure efficient resource utilization, load balancing, and high availability in cloud-native environments.
Automation
- Automation plays a crucial role in cloud-native solutions by streamlining repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and improving efficiency.
- Automated processes for testing, deployment, and monitoring enable rapid delivery of features and updates in a scalable manner.
Security
- Cloud-native security measures are essential to protect applications, data, and infrastructure in dynamic and distributed environments.
- Implementing security best practices, encryption, access control, and monitoring helps ensure the scalability and integrity of cloud-native solutions.
Implementing Cloud-Native Solutions for Scalable Growth
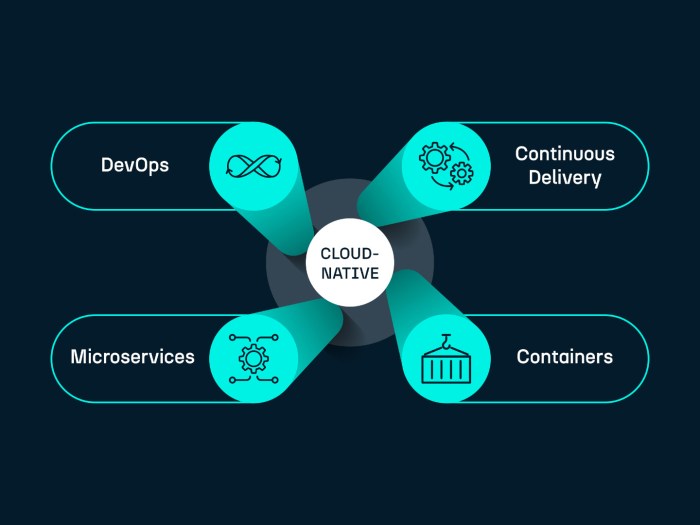
Implementing cloud-native solutions for scalable growth involves migrating existing applications to cloud-native architecture, developing applications using cloud-native principles, and selecting the right cloud platform for hosting these applications.
Migrating Existing Applications to Cloud-Native Architecture
Migrating existing applications to cloud-native architecture requires breaking down monolithic applications into microservices, containerizing these microservices using technologies like Docker, and orchestrating them with platforms like Kubernetes. This process allows for more flexibility, scalability, and resilience in the application architecture
Best Practices for Developing Applications Using Cloud-Native Principles
- Design applications with a microservices architecture to enable independent scaling and deployment of each component.
- Embrace automation for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to ensure faster delivery of features.
- Implement DevOps practices for collaboration between development and operations teams to streamline the deployment process.
- Utilize cloud-native technologies like serverless computing for efficient resource utilization and cost optimization.
Comparing Different Cloud Platforms for Hosting Cloud-Native Applications
When selecting a cloud platform for hosting cloud-native applications, consider factors such as:
- Compatibility with cloud-native technologies like Kubernetes and Docker
- Scalability and flexibility in resource allocation
- Pricing models and cost-effectiveness
- Security measures and compliance certifications
Popular cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer robust services for hosting cloud-native applications, each with its own strengths and capabilities.
Managing Scalability with Cloud-Native Solutions
Scalability is a crucial aspect of any modern digital infrastructure, and cloud-native solutions offer unique capabilities to manage scalability effectively.
Auto-Scaling for Dynamic Workloads
Cloud-native solutions enable auto-scaling, allowing systems to automatically adjust resources based on workload demands. This dynamic scaling ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Role of Monitoring and Analytics
- Implement robust monitoring tools to track system performance and resource utilization in real-time.
- Utilize analytics to identify trends, patterns, and potential bottlenecks that could impact scalability.
- Proactively address issues based on data-driven insights to maintain a scalable infrastructure.
Ensuring High Availability and Fault Tolerance
- Design applications with redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous availability.
- Implement load balancing and distributed architectures to distribute traffic and mitigate single points of failure.
- Utilize container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes to manage and scale applications seamlessly across multiple nodes.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, Cloud-Native Tech Solutions for Scalable Growth pave the way for a future where businesses can thrive and expand with agility and resilience.
Answers to Common Questions
How does cloud-native technology differ from traditional approaches?
Cloud-native technology focuses on building applications specifically for the cloud environment, utilizing containers and microservices for enhanced scalability and efficiency, unlike traditional monolithic architectures.
What are some best practices for developing applications using cloud-native principles?
Some best practices include designing applications as modular microservices, utilizing continuous integration and deployment pipelines, and implementing robust monitoring and logging for enhanced visibility.
How do cloud-native solutions enable auto-scaling for dynamic workloads?
Cloud-native solutions utilize orchestration tools like Kubernetes to automatically adjust resource allocation based on workload demands, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.